Video indexing sits at the front of modern media work. Video indexing turns every frame into structured data you can search, sort, and ship. When you place tags on speech, faces, logos, objects, and sentiment, editors find the right clip in seconds, ad ops match brands to moments that sell, and compliance teams show proof without a scramble. This guide explains how video indexing and search work, why they matter, what real teams do with them, and how to build a plan that fits your library.
Understanding Video Indexing
Video indexing assigns time-coded metadata to the pictures and sound inside a file so your team can search by what happens on screen, not by a file name. The process blends transcription, object detection, logo detection, optical character recognition, and language models. The result drives highlight reels, ad separation checks, and fast video retrieval for any team that touches content.
Indexing Videos vs. Cataloging Files
Cataloging stores a title, a date, and a few notes. Indexing videos adds timestamps, keyframes, and metadata tags that track people, places, and action. This richer layer shrinks search time and reduces rework.
Indexes Video With Context
Strong indexes video with context from audio, video, and text. A good index knows the speaker, the topic, the crowd mood, and the on-screen graphics. That context powers better recommendations and safer ad placement.
What Is Video Indexing?
Video indexing converts raw pixels and audio waves into fields that a database can query. Each tag ties to a timestamp. When someone types a query such as “coach press conference,” the system returns the exact start time and a jump link. That structure fuels instant jump-to-scene features, smart summaries, and playlists that stay on message.
The Building Blocks: Data, Metadata, and Keywords
Data holds the pictures and sound. Metadata describes that data. Keywords guide retrieval. You combine the three to build a search layer that covers every clip, live stream, and edit.
Why Models Matter
AI models drive recognition quality. Teams train models on their own footage to raise precision and recall. Sports, news, talk shows, and animation each need different training sets to hit target accuracy.

The Evolution of Indexing
Early crews kept log sheets with minute marks and broad themes. Spreadsheets replaced clipboards, but people still did the heavy lift. Speech-to-text engines added speed but left faces, logos, and screen text out. Current systems use artificial intelligence across sight and sound. A single pipeline runs transcription, object detection, logo detection, and OCR on the same asset. Open APIs let your MAM, newsroom, and cloud tools call the same index.
From Manual Notes to AI
Manual notes gave control but missed scale. AI brings scale and consistency. You still review results, but you do not start from scratch.
The Modern Indexer
A modern indexer ingests files, creates shot boundaries and keyframes, generates a transcript, and aligns each token to a timestamp. It also finds on-screen text, known faces, and brand marks. It then stores everything in a database that your apps can query.
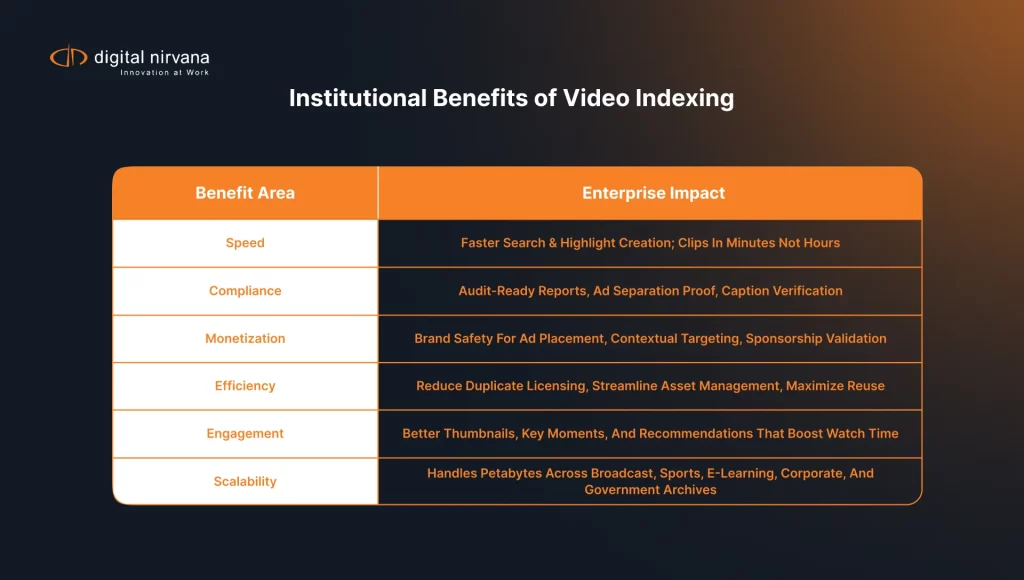
Video Indexing and Search: Why It Matters
Search sits at the center of every media workflow. Once your videos carry rich metadata, everyone moves faster.
Faster Content Discovery
Producers skip long scrubs. They search a term, filter by speaker, and jump to the moment that matters. That speed helps newsrooms beat the clock and helps creators publish more.
Smarter Media Asset Management
Asset managers deal with petabytes. Video indexing and search narrow results to only the shots that fit. Editors pull the best option from the archive instead of buying a duplicate license.
Compliance and Monitoring Support
Regulators ask for proof. Indexing pairs with monitoring to verify ad separation, captions, and loudness. Teams export a video indexing report that lists criteria, usage, and timestamps so audits take minutes, not days.
Core Capabilities in Modern Video Indexing
Modern platforms package several recognition engines into one workflow. Each engine adds a layer that improves retrieval.
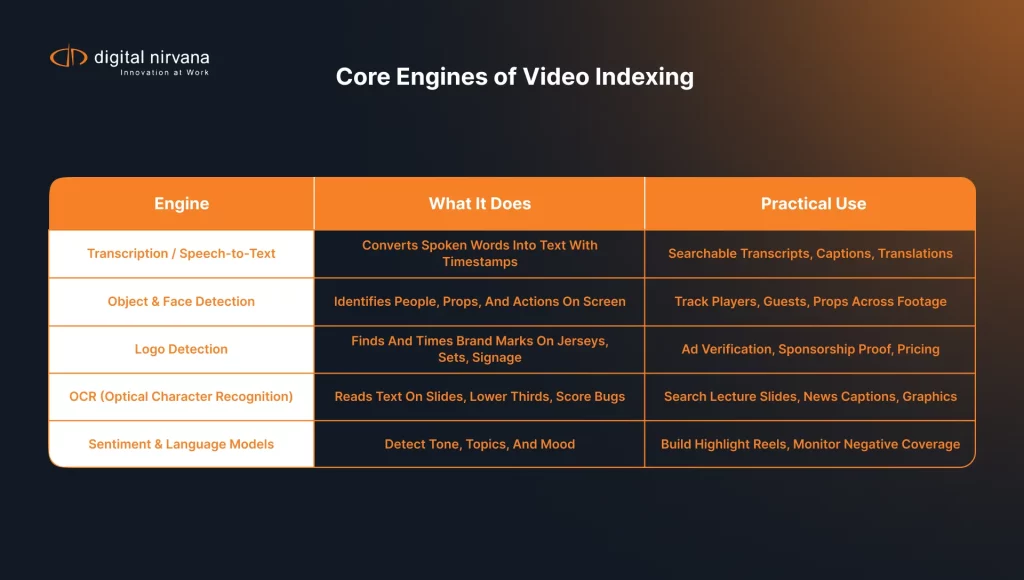
Transcription and Speech-to-Text
Transcription turns speech into text with speaker labels and punctuation. You search the transcript like a document. You also feed the text to closed captions and translation.
Practical Tips
Use domain language packs for names and jargon. Add a custom vocabulary list for team names, product lines, and slang. Review the first week to tune confidence thresholds.
Object Detection and Face Search
Object detection finds people, props, and scenes. Face search links appearances across episodes and seasons. Editors can trace a guest, a ball carrier, or a prop through many hours of footage.
Keyframes and Thumbnails
Set keyframes at shot changes. Use the best keyframe as the video thumbnail image. Strong thumbnails raise user engagement and retention on YouTube and on your own site.
Logo Detection and Brand Safety
Logo detection tracks marks on jerseys, backdrops, and signage. The system measures on-screen time and placement. Ad ops teams use this data to price sponsorships and confirm delivery.
Optical Character Recognition on Video Data
OCR reads lower thirds, score bugs, and slides. The text becomes searchable metadata. That ability matters for lecture capture, town halls, and product demos where slides carry the facts.
Language and Sentiment Analysis
Language models score tone and subject. Sports teams use sentiment spikes to build hype reels. News desks flag negative tone for deeper review.
How Video Indexing Works
Behind a simple search box sits a chain of steps that turns pixels into structured info.
Ingest, Analysis, and Timestamps
The indexer ingests a file or stream, then splits it into frames and audio chunks. Models scan frames for faces, text, and motion. The system aligns every tag to a timestamp. That alignment lets you lift clips with surgical precision.
Temporal Metadata and Ranges
Each entity carries a start and end time. Editors use the ranges to build highlight reels and chapters. OTT players read the same ranges to power seek bars and chapter lists.
Topic Clusters and Summary Markup
The engine groups tags into clusters such as goal, press conference, and product launch. It also creates a summary from the transcript. That summary markup improves the way search results appear on your site and helps internal users skim a long recording.
Index of /video and Crawlable Archives
Teams that manage public sites often publish archives. A simple index of /video page helps crawlers find content. Pair the listing with video schema markup, a video url field, and clean file names. Add a short summary and a thumbnail for each entry. That structure feeds Google search and your own on-site search.
File Format and Formats That Help Search
Store mezzanine files in a house format, then transcode to delivery formats for each channel. Keep sidecar files such as JSON or XML for the index. The file format needs to carry timecode cleanly.
Video Tagging for Accessibility
Add captions, transcripts, and audio descriptions to meet accessibility law and to serve your audience. Easy access grows reach on LinkedIn, YouTube, and your own app.
Models That Improve Accuracy
Your choice of models controls your results. Start with a baseline and tune over time.
General Models vs. Domain Models
General models work out of the box. Domain models learn the faces, jargon, and camera angles that your shows use. Sports and news crews get big gains from domain training.
Audio AI and Noise Handling
Microphones in crowds or on the field pick up noise. Audio AI filters crowd roar and music beds. A clean track improves the transcript and every downstream tag.
Model Scorecard
Track precision, recall, and false positives by tag type. Create a monthly video indexing report that shows quality trends and the clips you used in your gold set.
Applications Across Industries
Video indexing touches every industry that records video.
Broadcast and Media
Networks speed up clip pulls and build searchable archives for documentaries and retrospectives. Producers feed tickers and build rough cuts from search results.
Sports and Highlights Editing
Automated detectors find goals, touchdowns, or boundaries as they happen. Coaches pull plays by player and situation. Social teams post highlight reels at the break, not after the final horn.
Corporate Training and Knowledge Management
HR teams index policy talks and onboarding. Employees search a question and jump to the answer. Executives skim town halls by topic and action item.
E-learning and Academic Portals
Universities add slide OCR and term tagging. Students jump to a formula instead of scrubbing a two hour lecture. Researchers analyze speaking trends by discipline.
Legal and Law Enforcement
Body-cam and courtroom footage carries key facts. Indexing highlights suspect appearances and spoken keywords. Teams build case clips with chain-of-custody notes.
Government and Public Archives
Agencies digitize speeches and hearings. Indexing opens the collection to the public. Scholars pull scenes by person and topic without special tools.
Video Indexing for Monetization
Indexing does more than save time. It earns money when you align scenes and audiences.
Contextual Ad Insertion
Brand-safe tags tell ad servers which scenes fit a campaign. Platforms place coffee spots during calm morning segments and action games during high-energy moments.
Stronger Recommendations and Retention
Streaming services feed indexed data into recommenders. Better matches reduce churn. When viewers find what they like, session length and retention rise.
Licensing and Syndication
Rights teams search indexes for reusable clips. They package offers with timecodes and context. Metadata confirms exclusivity windows and prevents misuse.
Integrating Video Indexing Into Workflows
Adoption only works when the index sits where people already work.
API Access and Platform Integration
Expose REST or GraphQL endpoints that push tags to your newsroom, OTT CMS, and data lake. Developers script rough cuts straight from search results.
Compatibility With MAM Systems
Export indexes as JSON, XML, or MPEG-7. Attach sidecars to assets inside Avid MediaCentral or a cloud MAM. Editors see a timeline of tags inside their panels and drag selects to a sequence.
Cloud, On-Prem, and Hybrid
Cloud services scale for big events. On-prem clusters meet strict data rules. Many teams choose hybrid. They stage sensitive clips locally and burst compute to the cloud when demand spikes.
Digital Nirvana Advantage
Our team blends AI with human review inside MetadataIQ and MonitorIQ. We tag speech, faces, logos, objects, and on-screen text with frame-accurate timecodes. Editors view tags inside Avid panels and publish without extra exports. MonitorIQ keeps an auditable trail so your indexed tags stand up during review. If you want a walk-through, reach out for a short session. We will show a real index from ingest to search.
Real-World Lift You Can Measure
Clients cut turnaround time in half after they index a back catalog. Archive reuse climbs, duplicate purchases drop, and clip packages ship on time. Compliance teams answer ad separation questions with a single export.
Security, Authorization, and Privacy
Indexing only works when people trust the data and the access model.
Authorization and Roles
Give editors search access and give a smaller group the right to approve model changes. Log every sensitive query. Keep biometric search behind a gate.
Privacy by Design
Blur minors and bystanders in crowded scenes. Respect takedown requests. Set a clear retention policy for face vectors and training data.
SEO and Distribution Wins From Indexing
Strong indexes boost discoverability in Google search and inside your own site.
Markup That Helps Google
Publish a page per video with schema markup that includes the video url, duration, and a transcript summary. Add a thumbnail image and a clean title. Google often shows a key moment list when it finds timestamps in the transcript.
How LinkedIn and YouTube Benefit
On LinkedIn, a tight summary and a relevant thumbnail lift click-through. On YouTube, chapters built from timestamps improve watch time and session depth. Both platforms reward clear metadata and accurate captions.
Azure Video Indexer, Google Cloud, or Build Your Own
Many teams ask about tools. You can use a platform from Microsoft Azure, use Google Cloud APIs, or build a pipeline that mixes open source with hosted models. Each path can work.
When Azure Video Indexer Fits
You want a fast start and built-in dashboards. You accept a managed service and plan for cost at scale.
When a Custom Pipeline Fits
You need tight control over models, privacy, and cost. You have engineers who can manage inference, storage, and updates. You still use hosted GPUs for burst loads.
Data Design: Database and Retrieval
Your index stores millions of tags. Design the store for search speed and low cost.
Storage Choices
Use object storage for media and a search index for metadata. Keep hot content on fast tiers. Move cold archives to cheaper tiers with lifecycle rules.
Query Patterns
Most users search by person, topic, or event. Precompute facets for the top fields to keep results snappy. Cache common queries during big events.
Video Indexing Requirements and Rollout Plan
Set clear goals before you run a single file. A simple plan keeps the project on track.
Criteria and Success Metrics
Pick precision and recall targets for speech, face, and logo. Define review time per hour of content. Track search time saved per user per week.
Phased Rollout
Phase 1 covers high-value shows. Phase 2 covers the back catalog. Phase 3 adds live. Each phase closes with a video indexing report and a retro that lists wins and fixes.
Human Review That Scales
AI gets you close. Human review closes the gap.
Triage Workflow
Flag low-confidence tags. Assign them to reviewers in a queue. Reviewers correct, approve, or reject. The system learns from each action.
Playbook for Editors
Teach editors three moves. Search, jump, and lift. Search a term, jump to the moment, and lift the clip to the timeline. Keep it simple and adoption grows.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
You can dodge most issues with a little planning.
Over-Indexing
Do not tag every frame with every label. Pick the tags that drive real tasks. Extra noise slows search and hides the good stuff.
Ignoring Thumbnails
A weak thumbnail hurts discovery. Pick a keyframe that shows action and faces. Test thumbnails for click-through on your top pages.
Skipping Model Updates
Language shifts. Jerseys change. Update vocab lists and face galleries every quarter. Put it on the calendar.
Reporting That Proves Value
Leaders fund what they can measure.
Monthly Video Indexing Report
Ship a short deck each month. Include accuracy by model, search time saved, archive reuse, and revenue tied to indexed clips. Add a summary and a simple chart. Keep it readable.
Dashboards for Daily Use
Expose counters in a shared dashboard. Show new assets indexed, average time to first tag, and top queries. Display a feed of failed jobs so ops can act fast.
Real Stories From the Floor
Teams share a few patterns that make a difference.
The Live Sports Flip
A regional network moved from manual loggers to AI-assisted indexing. Producers built halftime reels from search results instead of memory. Social clips posted before the start of the third quarter. Ratings in that window rose.
The Lecture Library Fix
A university indexed ten years of lectures. Students searched by formula, not by course code. Watch time climbed and course forums saw fewer repeat questions.
The Brand Audit Win
A sponsor asked for proof of on-screen time across a season. The logo detection report listed every appearance with timestamps and keyframes. The renewal closed in one meeting.
Digital Nirvana, In Practice
At Digital Nirvana, we pair AI with people. MetadataIQ handles transcription, OCR, and detection. Our team tunes models for your domain and adds a human check where it counts. MonitorIQ tracks air checks and keeps an audit trail. We keep the workflow simple so your editors can focus on the story.
A Quick, Useful CTA
If you want a ten minute look at a working index, ask for a short demo. We will use your content, not a canned clip, and we will send you the report we create.
Future Trends You Can Plan For
The field keeps moving, but a few trends look durable.
Real-Time Indexing at the Edge
Small inference boxes at venues run light models and add tags before the stream hits the encoder. That setup cuts clip time for live shows.
Multilingual Indexing
Models now support more languages and dialects. Regional teams index and caption in the language their audience speaks. Cross-lingual tags map the same event in many tongues.
Richer Context
Next-gen models connect on-screen cues to the story arc. Tags like plot twist and comic relief help recommenders and brand safety filters.
Glossary for New Teammates
New joiners move faster with a shared glossary.
Video Data
The pixels and audio in a clip.
Metadata Tags
Labels that describe the content and link to timestamps.
Indexer
The engine that creates the index and writes sidecar files.
Video Retrieval
The act of finding the exact moment you want and lifting it for use.
Metadata Graph
A network that shows how clips, people, and topics connect. Some teams simply tag this as metadata g in internal docs.
Conclusion: Indexing That Drives Real Work
Video indexing gives every frame a job. Your team edits faster, your library earns more, and your compliance work holds up under review. Start with clear goals, train models on your domain, and put the index inside the tools your editors use every day. Run a phased rollout, keep thumbnails sharp, and publish a simple report each month. When your footage becomes searchable by what happens on screen, stories move with less friction and viewers stick around longer.
FAQs
What is video indexing in plain terms?
Video indexing means the system tags what happens in a video and ties each tag to a timestamp. You can search those tags like you search text, then jump to the exact moment.
How do I start indexing videos without a big rebuild?
Pick one high-value show. Run transcription, OCR, face search, and logo detection. Load the sidecar into your MAM and train a small group to use search and jump-to-scene. Expand after a two week trial.
Which AI models help most?
Speech-to-text models help every team. Sports and news groups gain from face and logo models. Lecture capture gains from OCR. Start with these three and add sentiment when you need highlights.
Will Google search show my key moments?
If you publish a page with a transcript, timestamps, a clean video url, and a thumbnail image, Google often shows key moments. Results vary by site and query, but good markup helps.
Is Azure Video Indexer the only option?
No. Microsoft offers a strong platform. Google Cloud offers APIs. You can also build a pipeline with open tools. Your choice depends on cost, privacy, and staffing.




