Media indexing turns raw footage and stills into searchable gold.
Automated engines tag every scene with faces, dialogue, and on‑screen text so editors hop straight to the perfect shot.
Rights teams pull compliance clips in minutes instead of days.
Streaming platforms surface the right thumbnail that keeps viewers watching longer.
Marketing crews reuse evergreen footage without blowing budgets on reshoots.
Read on to learn how indexing works, why it matters, and the fastest way to roll it out.
What Is Media Indexing and How It Works
Media indexing assigns descriptive, machine readable tags to every video, image, and audio file so any user can locate precise moments within seconds. It maps speech, faces, on-screen text, and objects to exact timecodes that search engines can parse without friction. Good indexing uses a clear schema and controlled terms so results stay consistent from ingest to archive. Teams see faster edits on day one and cleaner compliance pulls in week one because the right clip appears the moment they search. For a deeper primer, read The Power of Video Indexing for Smarter Content Search on Digital Nirvana’s blog.
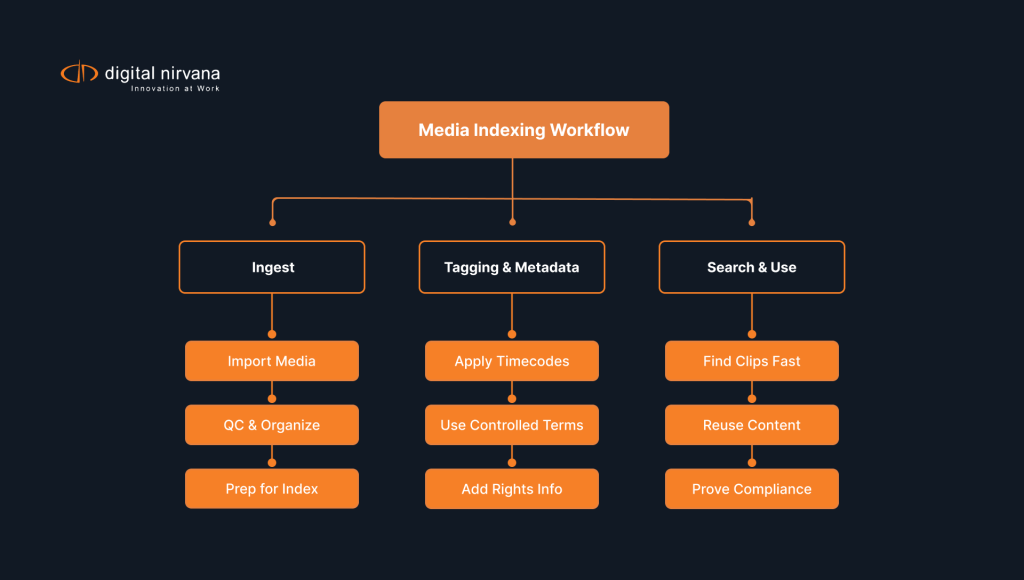
Definition of Media Indexing
Media indexing means attaching structured metadata to time‑based media. Each frame or segment receives labels about who appears, what they say, where the action occurs, and why the shot matters. An index differs from a simple folder name because search engines can parse the fields instantly. Broadcasters rely on indexes to surface archival footage while news is still breaking. Marketers use the same approach to keep campaigns on message without starting from scratch.
Our services at Digital Nirvana make indexing practical
Our services at Digital Nirvana help you stand up indexing without ripping or replacing your stack. MetadataIQ connects to your MAM and writes time coded speech, face, and logo tags that editors search inside Avid and Adobe. MonitorIQ records linear and OTT feeds around the clock and preserves a proof grade archive your legal and ad ops teams can search on demand. TranceIQ generates transcripts and captions that become rich metadata for every clip, which boosts findability and compliance. If you want to move fast, book a short walkthrough to see how these tools fit your taxonomy and workflows.
Why Media Indexing Is Important for Your Media Library
Media libraries grow at a pace that buries good footage if teams rely on folders and file names. A robust index turns large archives into living libraries that answer concrete questions such as who spoke, what was on screen, and when it happened. Editors, producers, and legal staff gain the same single source of truth, which reduces rework and missed deadlines. Accurate indexing also improves personalization and analytics because downstream systems consume the same clean data. The payoff shows up in faster cuts, fewer reshoots, and fewer compliance surprises.
Faster Content Discovery and Retrieval
Searchable indexes cut retrieval time from hours to seconds. Editors jump directly to a key quote or reaction shot instead of browsing entire reels. Rights managers produce proof of compliance for regulators on deadline. Speed gains free creative teams to focus on storytelling rather than file hunting.
Better Compliance and Rights Management
Accurate indexes document who appears, what music plays, and where footage originated. Legal teams answer clearance questions quickly, preventing costly takedowns. The archive records usage rights so producers avoid accidental violations. Strong logs also support caption and loudness checks that regulators expect. For context on caption rules in the United States, see the Federal Communications Commission consumer guide.
Enabling AI‑Powered Metadata and Search
AI thrives on clean data. A well‑structured index feeds recommendation engines, content reuse dashboards, and automatic highlight reels. As AI models evolve, they enrich existing metadata rather than starting over, compounding value over time.
Key Terms Related to Media Indexing in Today’s Media World
Media indexing comes with a shared language that keeps projects aligned. Teams that define terms at kickoff avoid confusion later when clips move from rough cut to air. A helpful reference describes three broad metadata types, descriptive, administrative, and structural, outlined by the Library of Congress metadata overview. Common definitions shorten onboarding for new editors and vendors. Use this section to calibrate how your organization talks about data in daily work.
Metadata
Metadata is data about data. In media, it covers technical info such as resolution, creative descriptors like mood, and administrative details including rights. Rich metadata drives search relevance and personalization.
Taxonomy and Ontology
A taxonomy is a hierarchical list of categories, while an ontology maps relationships between those categories. Together they give indexing engines a clear blueprint so results stay consistent across projects.
Tagging vs Indexing
Tagging places quick labels on assets, often freestyle and inconsistent. Indexing follows a formal structure with defined fields, controlled vocabularies, and timecodes. Indexing delivers precision at scale that ad‑hoc tags cannot match.
Controlled Vocabularies
Controlled vocabularies limit the terms users can apply, reducing spelling errors and synonym drift. They ensure that a search for “soccer” returns the same footage that a producer labeled “football” in another region. Advance indexing softwares with robust algorithm update and adapt to these local nuances.
Benefits of Media Indexing for Broadcasters, OTT, and Brands
Media businesses share a need for speed, accuracy, and reuse, and a strong index touches each area. Producers find the exact quote or shot in seconds, sales verifies ad delivery with proof clips, and legal exports compliance logs without pulling engineers off live duties. Marketing reuses evergreen content across platforms because search surfaces assets already on disk. For a revenue angle, see The Role of Metadata in Content Monetization Strategies on our blog. Below are practical benefits teams report after rollout.
Streamlined Post‑Production Workflows
Editors use shot lists generated from index data to assemble rough cuts fast. Automated subclipping lets assistants deliver selects without manual review. Projects hit deadlines even as teams juggle multiple versions.
Enhanced Audience Experience Through Personalization
Streaming services match viewers with scenes featuring favorite actors or topics by querying indexes. Personalized playlists boost watch time and reduce churn.
Reduced Operational Costs
Efficient search reduces storage waste by exposing existing assets for reuse. Teams avoid duplicate shoots and licensing fees, stretching budgets further.
Popular Media Indexing Methods and Best Practices
Choosing an approach means balancing accuracy, cost, and speed while planning for growth. Many teams begin with automation to cover scale, then add human review where the model confidence dips. Industry benchmarks such as the NIST TRECVID program show how video indexing methods get tested and compared over time. For practical how to guidance, our AI metadata tagging guide outlines workflows and tuning ideas you can apply this quarter. The methods below are the ones most teams use in production.
Automated AI Indexing
AI platforms handle enormous libraries by analyzing video, audio, and text simultaneously. They deliver speed and scale, with accuracy improving as models learn from feedback. Continuous training keeps results sharp.
Manual Curation and Quality Control
Human specialists verify and enrich AI output, adding context that automation might miss. Their judgment ensures critical footage carries precise labels, especially for niche subjects.
Hybrid Approaches
A hybrid model marries AI speed with human oversight. Systems flag confidence scores, and curators focus on low‑confidence segments. The mix achieves high accuracy without bottlenecks.
Step‑by‑Step Guide to Start Indexing Your Media Collection
Teams succeed when they start small, measure early, and scale in phases. Begin with one show, one franchise, or one campaign so you can prove time saved and clips found before expanding. Share visible wins with leadership and capture before and after metrics for retrieval time and reshoot avoidance. Pair a pilot with staff training so editors tag consistently from day one. For background on why metadata drives discovery, read How Impactful Is Video Metadata for Discoverability and User Engagement on our blog.
Audit and Organize Existing Assets
Start by cataloging every storage location, file type, and rights agreement. Consolidate duplicates and delete obsolete files. A clean slate prevents garbage‑in results later.
Choose an Indexing Taxonomy
Draft a taxonomy that reflects your business goals, genres, people, brands, or campaign codes. Keep it shallow enough for quick adoption yet detailed enough for deep search.
Select Tools and Platforms
Evaluate solutions based on library size, existing workflows, and integration needs. Cloud platforms offer elastic compute for video analysis, while on‑premise gear meets strict security rules.
Train Your Team and Monitor Quality
Run workshops so editors, archivists, and legal staff apply terms consistently. Set up dashboards that track indexing accuracy and retrieval times. Continuous feedback keeps the system sharp.
Media Indexing vs Tagging vs Cataloging: Key Differences
Teams often mix these terms, which raises expectations and causes misses in handoffs. Use this section to draw clean lines so every role knows what to deliver. Tagging gives quick labels for social posts, indexing ties labels to timecodes for frame accurate search, and cataloging describes containers across a collection. Workflows run smoother when each layer stays in its lane and feeds the next. If you want examples of search tied to monitoring and compliance, see our post on broadcast oversight.
Scope and Depth of Metadata
Tagging uses quick labels, indexing applies structured terms with timecodes, and cataloging describes an entire collection at the container level. Each layer serves unique search needs.
Use Cases and Workflow Impact
Tagging helps social teams find highlights, indexing powers frame‑accurate search for editors, and cataloging guides archivists through legacy tapes. Clear boundaries stop confusion and duplication of effort.
How Digital Nirvana Supports Media Indexing at Scale
Digital Nirvana designs solutions that shorten the path from raw footage to finished stories for editors, marketers, and compliance teams. Our platform approach combines indexing, monitoring, and captioning so teams do not juggle disconnected tools. We integrate with popular MAM systems and support hybrid deployments that meet strict security rules. Customers adopt in phases with clear milestones so value appears fast and risk stays low. The sections below highlight how our core products handle indexing in daily work.
Overview of MetadataIQ and MonitorIQ Indexing Features
MetadataIQ automatically ingests content, extracts speech, detects faces, and writes searchable metadata to major MAM systems. MonitorIQ captures broadcast feeds, indexes them in real time, and lets compliance teams pull clips through a browser. Together they provide end‑to‑end coverage from production to air.
Real‑World Use Cases
Major broadcasters use MetadataIQ to tag news footage overnight so morning editors cut packages faster. Sports networks rely on MonitorIQ to verify ad playout and prove compliance. Brands with large social channels repurpose historical clips thanks to precise indexes.
At Digital Nirvana, we help you index at scale
At Digital Nirvana, we help you turn indexing from a pilot into a reliable operation. Our engineers map your taxonomy, connect ingestion to MetadataIQ for automated tags, and set MonitorIQ to capture airchecks and OTT streams for searchable retention. We pair automation with editorial review so high value content receives human polish without slowing delivery. We also offer closed captioning services that meet every rule and feed fresh data back into your library. Ask for a phased rollout plan that shows time saved and search wins in the first month.
In summary…
A clear index gives every team a faster way to find, reuse, and prove. This short recap pulls together the ideas you can act on right away. Share it with editors and legal so everyone speaks the same language and trusts the same records. Consider a pilot on one show or campaign and measure retrieval time and reshoot savings. Then expand to more libraries with a simple taxonomy and a short training session.
- Indexing assigns structured, searchable metadata to every asset.
- Speed gains let editors, legal teams, and marketers find content in seconds.
- Taxonomies, ontologies, and controlled vocabularies keep terms consistent.
- AI handles bulk analysis, while human curators polish critical clips.
- Digital Nirvana’s MetadataIQ and MonitorIQ deliver indexing from ingest through compliance.
Implement these practices now to save time, cut costs, and serve audiences better tomorrow.
FAQs
Readers ask sharp, practical questions about media indexing every week. This section gathers the answers we give most often to editors, engineers, and marketing leads. Each reply stays focused on action you can take today rather than theory. If your scenario looks unique, use these as starting points and adapt the steps to your stack. You can also combine manual checks with automation as you mature.
What is the difference between media indexing and media tagging?
Indexing uses a defined schema, controlled vocabularies, and timecodes, while tagging often relies on freeform labels. Indexing supports precise, frame‑level search. Tagging suits quick categorization but lacks depth.
How long does it take to index a one‑hour video?
Automated engines process a one‑hour HD video in roughly real‑time on modern cloud infrastructure. Manual quality checks add extra minutes for high‑value content.
Do I need AI to start media indexing?
You can begin with manual indexing, but AI scales the effort across large libraries. Hybrid models give the best balance between speed and accuracy.
Which file formats benefit most from indexing?
All time‑based formats gain value from indexing, including MP4, MXF, MOV, and WAV. Even still images see gains when labeled with location, subject, and rights info.
How does Digital Nirvana price its indexing solutions?
Digital Nirvana offers subscription tiers based on volume and features. Contact the sales team for a tailored quote that matches your library size and workflow.